Integrating ACS into the Pipeline
Finally: Putting the Sec in DevSecOps!
There are basically two ways to interface with ACS. The UI, which focuses on the needs of the security team, and a separate “interface” for developers to integrate into their existing toolset (CI/CD pipeline, consoles, ticketing systems etc): The roxctl commandline tool. This way ACS provides a familiar interface to understand and address issues that the security team considers important.
ACS policies can act during the CI/CD pipeline to identify security risk in container images before they are started.
Integrate Image Scan into the Pipeline
You should have created and build a custom policy in ACS and tested it to trigger violations. Now you will integrate it into the build pipeline.
Our task will use the roxctl cli
Build-time policies require the use of the roxctl command-line tool which is available for download from the ACS Central UI, in the upper right corner of the dashboard. You don’t need to to download this now as our Tekton task will do this automatically.
roxctl needs to authenticate to ACS Central to do anything. You can use either username and password or API tokens to authenticate against ACS Central. It’s good practice to use a token so that’s what we’ll do.
Let’s Go : Create the roxctl token
In the ACS portal:
- Navigate to Platform Configuration > Integrations.
- Scroll down to the Authentication Tokens category, and select API Token.
- Click Generate Token. Enter the name
pipelinefor the token and select the role Admin. - Select Generate
- Save the contents of the token somewhere!
Create OCP secret with token
Change to the OpenShift Web Console and create a secret with the API token in the project your pipeline lives in:
- In the UI switch to your
workshop-intProject - Create a new key/value
Secretnamed roxsecrets - Introduce these key/values into the secret:
- rox_central_endpoint: <the URL to your ACS Portal> (without https:// but adding the port, e.g. entral-stackrox.apps.cluster-cqtsh.cqtsh.example.com:443)
- If the
DOMAINplaceholder was automatically replaced it should be: central-stackrox.apps.<DOMAIN>:443 - If not, replace it manually with your DOMAIN
- If the
- rox_api_token: <the API token you generated>
- rox_central_endpoint: <the URL to your ACS Portal> (without https:// but adding the port, e.g. entral-stackrox.apps.cluster-cqtsh.cqtsh.example.com:443)
Even if the form says Drag and drop file with your value here… you can just paste the text.
Remove ImageStream Change Trigger
There is one more thing you have to do before integrating the image scanning into your build pipeline:
When you created your deployment, a trigger was automatically added that deploys a new version when the image referenced by the ImageStream changes.
This is not what we want! Because this way a newly build image would be deployed immediately even if the roxctl scan detects a policy violation and terminates the pipeline.
Have a look for yourself:
- In the OCP console go to Workloads->Deployments and open the
workshopDeployment - Switch to the YAML view
- Near the top under annotations (around lines 11-12) you’ll find an annotation
image.openshift.io/triggers.
Remove exactly this lines and click Save:
image.openshift.io/triggers: >-
[{"from":{"kind":"ImageStreamTag","name":"workshop2:latest","namespace":"workshop-int"},"fieldPath":"spec.template.spec.containers[?(@.name==\"workshop2\")].image","pause":"false"
This way we make sure that a new image won’t be deployed automatically right after the build task which also updates the ImageStream.
Create a Scan Task
You are now ready to create a new pipeline task that will use roxctl to scan the image build in your pipeline before the deploy step:
- In the OpenShift UI, make sure you are still in the project with your pipeline and the secret
roxsecrets - Go to Pipelines->Tasks
- Click Create-> ClusterTask
- Replace the YAML displayed with this:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1beta1
kind: ClusterTask
metadata:
name: rox-image-check
spec:
params:
- description: >-
Secret containing the address:port tuple for StackRox Central (example -
rox.stackrox.io:443)
name: rox_central_endpoint
type: string
- description: Secret containing the StackRox API token with CI permissions
name: rox_api_token
type: string
- description: "Full name of image to scan (example -- gcr.io/rox/sample:5.0-rc1)"
name: image
type: string
- description: Use image digest result from s2i-java build task
name: image_digest
type: string
results:
- description: Output of `roxctl image check`
name: check_output
steps:
- env:
- name: ROX_API_TOKEN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: rox_api_token
name: $(params.rox_api_token)
- name: ROX_CENTRAL_ENDPOINT
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
key: rox_central_endpoint
name: $(params.rox_central_endpoint)
image: registry.access.redhat.com/ubi8/ubi-minimal:latest
name: rox-image-check
resources: {}
script: >
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set +x
curl -k -L -H "Authorization: Bearer $ROX_API_TOKEN"
https://$ROX_CENTRAL_ENDPOINT/api/cli/download/roxctl-linux --output
./roxctl > /dev/null; echo "Getting roxctl"
chmod +x ./roxctl > /dev/null
./roxctl image check -c Workshop --insecure-skip-tls-verify -e $ROX_CENTRAL_ENDPOINT
--image $(params.image)@$(params.image_digest)
Take your time to understand the Tekton task definition:
- First, some parameters are defined, it’s important to understand some of these are taken or depend on the build task that run before.
- The script action pulls the
roxctlbinary into the pipeline workspace so you’ll always have a version compatible with your ACS version. - The most important bit is the
roxctlexecution, of course:- it executes the
image checkcommand - only checks against policies from category Workshop that was created above. This way you can check against a subset of policies!
- defines the image to check and it’s digest
- it executes the
Add the Scan Task to the Pipeline
Now add the rox-image-check task to your pipeline between the build and deploy steps.
- In the Pipelines view of your project click the three dots to the right and the Edit Pipeline
Remember how we edited the pipeline directly in yaml before? OpenShift comes with a graphical Pipeline editor that we will use this time.
- Hover your mouse over
buildtask and click the + at the right side of it, to add a task - Click on Add task
- Then enter rox-image-check in the search box

Click image to enlarge
- Click the Add button to add to the pipeline
- To add the required parameters from the pipeline for the task so the ACS client can connect to central, click the rox-image-check task.

Click image to enlarge
- A form with the parameters will open, fill it in:
- rox_central_endpoint:
roxsecrets - rox_api_token:
roxsecrets - image:
quay-quay-quay.apps.<DOMAIN>/openshift_workshop-int/workshop(if theDOMAINplaceholder hasn’t been replaced automatically, do it manually) - Adapt the Project name if you changed it
- rox_central_endpoint:
- image_digest: $(tasks.build.results.IMAGE_DIGEST)
- This variable takes the result of the build task and uses it in the scan task.

Click image to enlarge
- This variable takes the result of the build task and uses it in the scan task.
- Don’t save yet
Add the oc patch Task to the Pipeline
As you remember we removed the trigger that updates the Deployment on ImageStream changes. Now the Deployment will never be updated and our new Image version will never be deployed to workshop-int.
To fix this we will add a new oc client Task that updates the Deployment, only after the Scan Task has run.
- While still in the visual pipeline editor
- Click on the + button to the left of the
deployTask - Click on Add Task
- In the search window enter
openshiftand select the openshift-client from Red Hat - Click on Add
- Click on the new
openshift-clientTask - In Task form on the right enter
- Display name : update-deploy
- SCRIPT :
oc patch deploy/workshop -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"containers":[{"name":"workshop","image":"$(params.QUAY_URL)/openshift_workshop-int/workshop@$(tasks.build.results.IMAGE_DIGEST)"}]}}}}'

Click image to enlarge
- Now save the pipeline
Test the Scan Task
With our custom System Policy still not set to enforce we first are going to test the pipeline integration. Go to Pipelines and next to your pipeline click on the three dots and then Start. Now in the pipeline startform enter java-old-image in the Version field.
- Expected Result:
- The
rox-image-checktask should succeed, but if you have a look at the output (click the task in the visual representation) you should see that the build violated our policy!
- The
Enforce the Policy
The last step is to enforce the System Policy. If the policy is violated the pipeline should be stopped and the application should not be deployed.
- Edit your custom System Policy
Workshop RHSA-2021:4904in ACS Portal and set Response Method to Inform and enforce and then switch on Build and Deploy below. - Run the pipeline again, first with Version
java-old-imageand then with Versionopenjdk-11-el7(default) - Expected results:
- We are sure you know by now what to expect!
- The pipeline should fail with the old image version and succeed with the latest image version!
- Make sure you run the pipeline once, otherwise your application will not have a valid image tag when you kill the running pod in the next chapter

Click image to enlarge
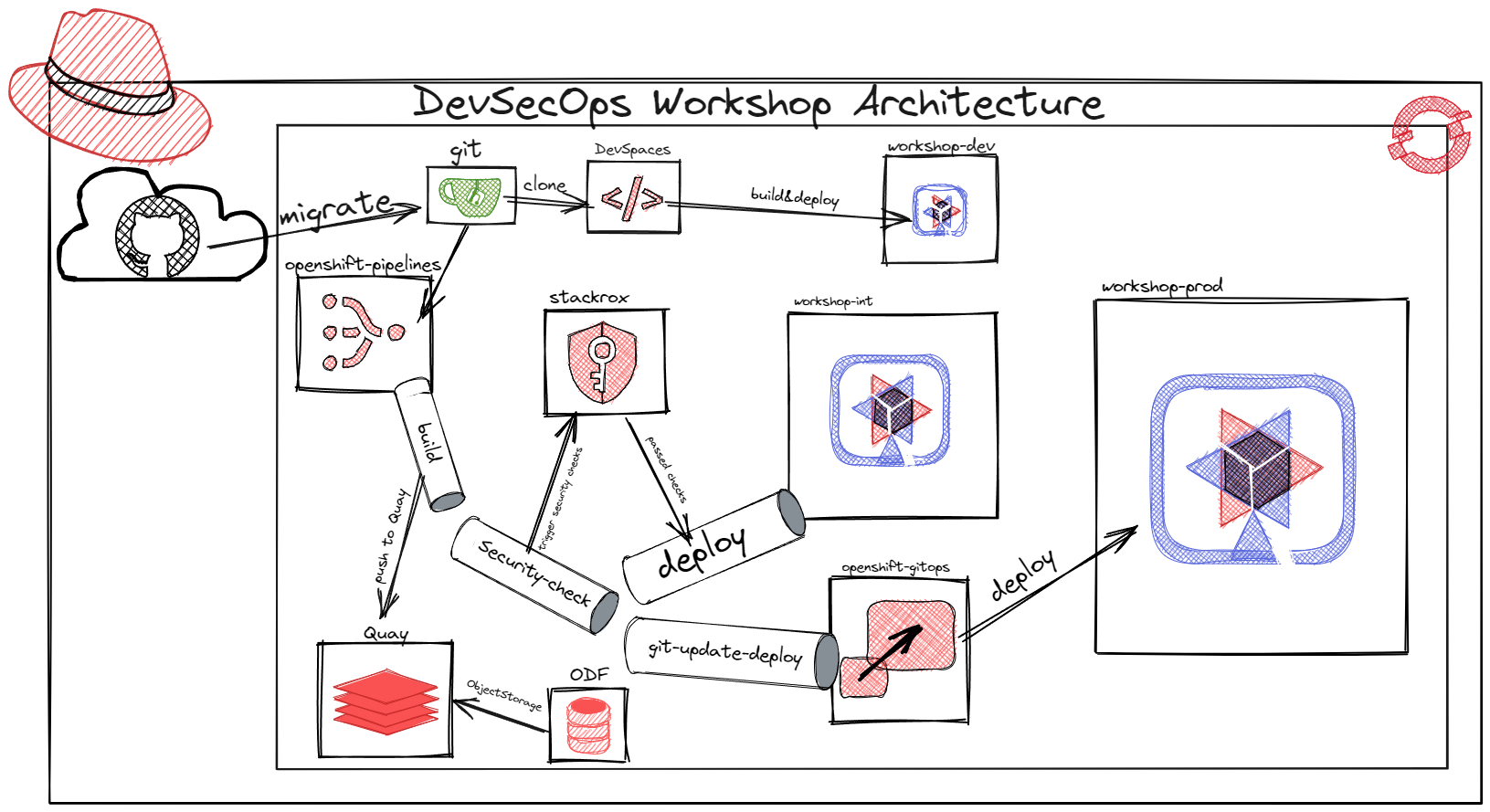
Architecture recap